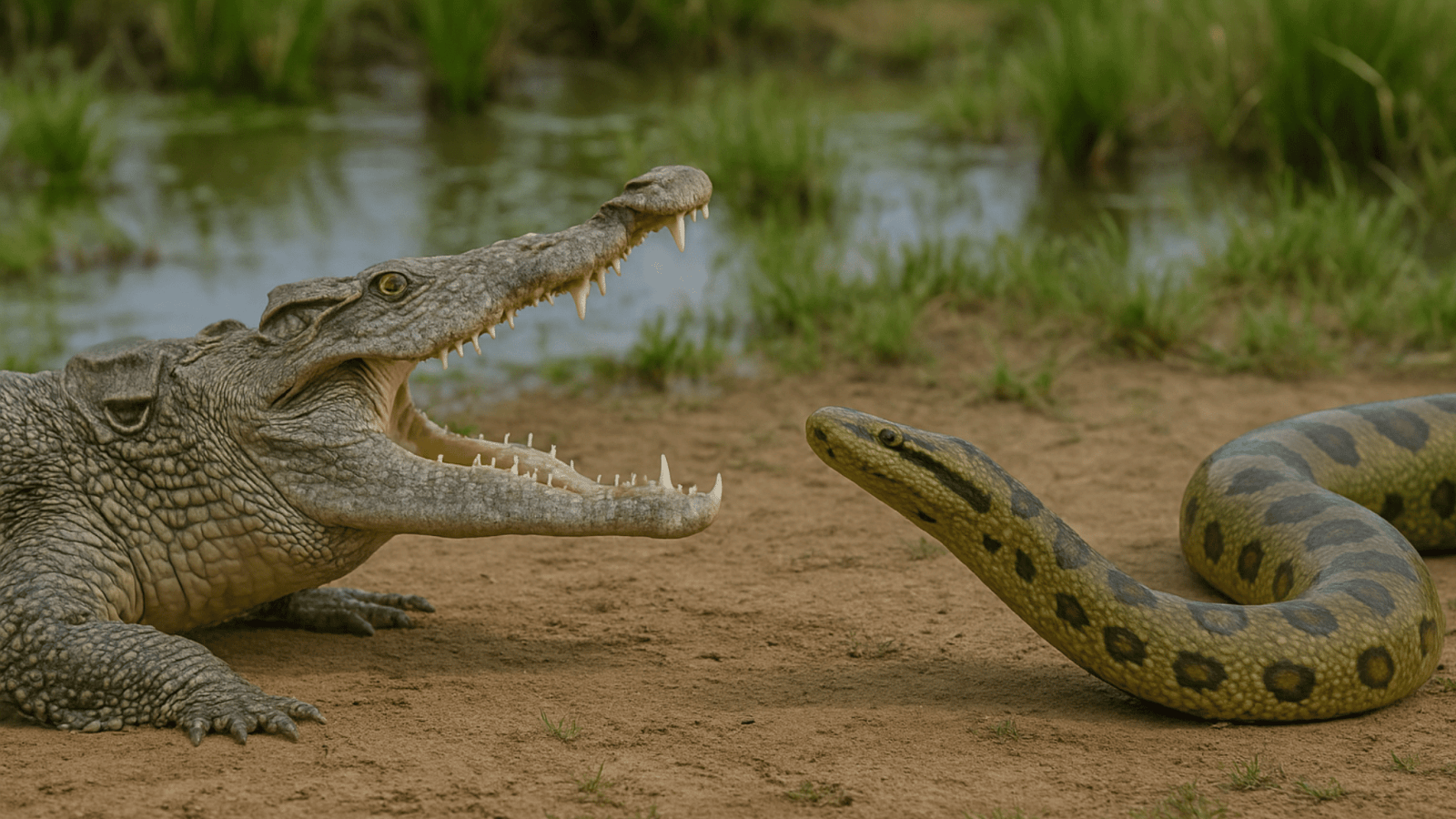
The Nile Crocodile Vs Anaconda, These two lives in murky waters of two different continents. Both 0f them are most fearsome reptilian predators on Earth: the Nile Crocodile of Africa and the Anaconda of South America. Both are master ambush predator, capable of overpowering massive prey with sheer strength and stealth.
While the Nile Crocodile relies on bone-crushing jaws and death rolls, the Anaconda uses its colossal body to crush prey. Anyway they would never meet in the wild, imagine if they meet each other and start to fight. Who would be the winner? With this article we dive deep into their biology, behavior, and battle tactics to discover who would win?
Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus)
green anaconda (Eunectes murinus)
So you will be able to know Who has the most advanced features as well as the battle potential. we’ll dive into 10 scientifically curated categories, each with 10 subtopics, and determine who wins in this ultimate clash.
Body Specifications
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 4.2–5.5 m | 4.5– 9m | Anaconda |
| Weight | 410–750 kg | 100–250 kg | Crocodile |
| Body Shape | Streamlined, armored | Cylindrical, muscular | Crocodile |
| Skin Thickness | ~1.5 cm | ~1.0 cm | Crocodile |
| Bone Density | High osteoderm content | Less dense vertebrae | Crocodile |
| Muscle Mass | Concentrated in tail and jaws | Distributed along the body | Crocodile |
| Skull Size | 65–75 cm | ~45 cm | Crocodile |
| Vertebrae Count | 65–70 | 200+ | Anaconda |
| Flexibility | Limited lateral flexion | Extreme flexibility | Anaconda |
| Overall Size Dominance | Larger in mass | Longer in length | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (6/10)
Skin & Camouflage – Nile Crocodile Vs Anaconda
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coloration | Olive, tan, dark bands | Green, black oval blotches | Anaconda |
| Pattern Utility | Breaks outline in water | Camouflages in swamp vegetation | Anaconda |
| Melanin Levels | Moderate | High | Anaconda |
| Shedding Frequency | Periodic | Frequent | Anaconda |
| Skin Function | Armor-like, protection | Flexible for constriction | Anaconda |
| Water Reflection | Glossy, reflective | Matte, minimal glare | Anaconda |
| Tactile Sensory Receptors | Integumentary sensory organs | Absent | Crocodile |
| Resistance to Parasites | High | Moderate | Crocodile |
| Heat Absorption | Excellent via basking | Slow heating | Crocodile |
| Camouflage Efficiency | In muddy rivers | In dense aquatic vegetation | Anaconda |
Category Winner: Anaconda (6/10)
Habitat and Range
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic Range | Sub-Saharan Africa | Amazon Basin | Draw |
| Preferred Habitat | Rivers, lakes | Swamps, slow rivers | Draw |
| Climate Preference | Tropical, semi-arid | Humid tropics | Draw |
| Habitat Versatility | Lakes, rivers, dams | Swamps, marshes | Crocodile |
| Aquatic Adaptation | Exceptional swimmer | Aquatic ambusher | Draw |
| Terrestrial Mobility | Moderate | Poor | Crocodile |
| Arboreal Capability | None | Can climb when young | Anaconda |
| Altitude Range | Lowland | Lowland | Draw |
| Water Hunting | Active | Ambush | Draw |
| Human Proximity Tolerance | High | Low | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (3), Anaconda (1), Draw (6) — Draw
Diet and Hunting Strategy
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Diet | Fish, antelope, buffalo | Fish, birds, caiman, deer | Draw |
| Max Prey Size | Zebras, buffalo | Capybara, deer | Crocodile |
| Ambush Technique | Death roll, jaw snap | Constriction | Draw |
| Hunting Success Rate | ~50% | ~70% (ambush) | Anaconda |
| Digestion Time | Days to weeks | Days to weeks | Draw |
| Hunting Frequency | Every few days | Weekly to biweekly | Anaconda |
| Teeth Structure | Conical, ~60–70 teeth | Backward-curved, non-venomous | Crocodile |
| Feeding Behavior | Opportunistic | Patient ambusher | Anaconda |
| Jaw Function | 2,000–5,000 PSI bite | Expansive gape | Crocodile |
| Prey Handling | Thrash & tear | Swallow whole | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (5), Anaconda (3), Draw (2) — Crocodile
Strength and Physical Power
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bite Force | 2,000–5,000 PSI | ~90 PSI (grip only) | Crocodile |
| Constricting Force | None | >90 kg/cm² | Anaconda |
| Tail Strength | High; can knock prey | High; used in swimming | Draw |
| Lifting Capacity | Limited | Can constrict large prey | Anaconda |
| Death Roll Power | Devastating | N/A | Crocodile |
| Skull Durability | Exceptionally thick | Fragile under pressure | Crocodile |
| Jaw Opening Range | Limited vertically | Extreme lateral gape | Anaconda |
| Endurance in Water | High | High | Draw |
| Explosive Strength | Massive lunge speed | Coiling burst | Draw |
| Resistance to Damage | Armored | Soft-bodied | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (5), Anaconda (3), Draw (2) — Crocodile
Speed and Agility – Nile Crocodile Vs Anaconda
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Land Speed | 12–14 km/h | 5 km/h | Crocodile |
| Top Water Speed | 30–35 km/h (burst) | 10–15 km/h | Crocodile |
| Acceleration | Moderate | Slow | Crocodile |
| Turning Radius in Water | Moderate | High flexibility | Anaconda |
| Reflexes | Fast | Moderate | Crocodile |
| Aquatic Agility | Strong bursts | Excellent for stealth | Anaconda |
| Climbing Ability | None | Can climb when young | Anaconda |
| Burrowing | None | Limited | Draw |
| Tree Navigation | No | Limited (juvenile) | Anaconda |
| Stamina in Hunt | Moderate | High | Anaconda |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (4), Anaconda (5), Draw (1) — Anaconda
Sensory Abilities – Nile Crocodile Vs Anaconda
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision (Day) | Excellent | Moderate | Crocodile |
| Vision (Night) | Good, tapetum lucidum | Poor | Crocodile |
| Hearing | Acute | Poor | Crocodile |
| Smell | Highly developed | Good | Crocodile |
| Touch Sensitivity | Integumentary receptors | General touch only | Crocodile |
| Heat Detection | Jaw sensors for thermal input | Absent | Crocodile |
| Lateral Line Analog | None | Vibration sensing | Anaconda |
| Underwater Vision | Excellent | Poor | Crocodile |
| Spatial Awareness | Excellent in water | Good in water | Crocodile |
| Reaction Time | Fast | Moderate | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (9), Anaconda (1) — Crocodile
Reproduction and Lifespan
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sexual Maturity Age | 10–12 yrs | 3–4 yrs | Anaconda |
| Reproductive Frequency | Every 1–2 years | Annually | Anaconda |
| Egg vs Live Birth | Oviparous (eggs) | Ovoviviparous (live) | Anaconda |
| Clutch/Litter Size | 25–80 eggs | 20–40 live young | Crocodile |
| Offspring Survival Rate | Low (~1%) | Low-moderate | Anaconda |
| Gestation/Incubation | ~90 days | ~6–7 months | Draw |
| Parental Investment | High (guards nest) | None | Crocodile |
| Lifespan (Wild) | 70–100 yrs | 10–30 yrs | Crocodile |
| Lifespan (Captivity) | Up to 100 yrs | ~30 yrs | Crocodile |
| Generation Time | Longer | Shorter | Anaconda |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (6), Anaconda (4) — Crocodile
Social Behavior
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Structure | Solitary or loosely gregarious | Solitary | Crocodile |
| Parental Care | Yes (nest guarding) | None | Crocodile |
| Mating Behavior | Competitive | Passive | Crocodile |
| Communication | Hisses, bellows | Hisses | Crocodile |
| Territoriality | Strong | Weak | Crocodile |
| Nesting Behavior | Constructs nests | None | Crocodile |
| Intra-species Conflict | High | Rare | Anaconda |
| Group Feeding | Common in carcass sites | Never | Crocodile |
| Intelligence | Moderate | Moderate | Draw |
| Learning Ability | Documented | Limited | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (9), Anaconda (0), Draw (1) — Crocodile
Conservation Status – Nile Crocodile Vs Anaconda
| Subtopic | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Status | Least Concern | Least Concern | Draw |
| Population Trend | Stable | Stable | Draw |
| Major Threats | Hunting, habitat loss | Habitat loss, pet trade | Draw |
| Legal Protection | CITES Appendix I/II | CITES Appendix II | Draw |
| Captive Breeding Success | High | Moderate | Crocodile |
| Public Perception | Feared and protected | Feared, sometimes hunted | Draw |
| Range Overlap with Humans | High | Moderate | Crocodile |
| Conservation Programs | Extensive | Moderate | Crocodile |
| Ecological Role | Apex predator | Apex predator | Draw |
| Endemism | Widespread Africa | Limited to South America | Crocodile |
Category Winner: Nile Crocodile (4), Draw (6) — Crocodile
Face-to-Face Fight Analysis: Nile Crocodile vs Anaconda
If the Nile crocodile and green anaconda were to clash in the water, several biological and behavioral factors would play key roles:
-
Location: In shallow swampy waters, the anaconda has a better chance due to stealth and constriction. In deeper, open water or near land, the crocodile dominates.
-
Opening Moves: The anaconda may attempt to ambush and constrict. But the crocodile’s armor, powerful tail, and devastating jaws make it hard to subdue.
-
Defense: The crocodile’s dermal scutes are near-impenetrable. Even if the anaconda begins constriction, the crocodile could perform a violent roll, break the coils, and snap the snake in two.
-
Outcome: Most likely, the crocodile will bite, thrash, and kill the anaconda before it can complete a coil.
Face-to-Face Fight Winner: Nile Crocodile
Final Conclusion: Who Wins — Nile Crocodile vs Anaconda?
| Category Wins | Nile Crocodile | Anaconda | Draw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 8 | 2 | 2 |
✅ Overall Winner: Nile Crocodile
Why Nile Crocodile Wins:
-
Superior bite force and armored body
-
Faster both in water and on land
-
Advanced sensory system and durability
-
Excellent parental investment and social traits
-
Consistently dominant across categories
Why Anaconda Loses:
-
Lacks armor and is more vulnerable
-
Relies solely on stealth and constriction
-
Slower, with weaker senses and bite
-
Lower lifespan and limited cognitive behaviors
Interesting Facts – Nile Crocodile Vs Anaconda
Nile Crocodile
-
Largest crocodile in Africa.
-
Can grow up to 6 meters long.
-
Weighs over 1,000 pounds.
-
Has the strongest bite in the animal kingdom.
-
Eats fish, mammals, birds, and sometimes other crocodiles.
-
Can survive months between meals.
-
Females lay up to 100 eggs at a time.
-
Excellent swimmer and ambush predator.
-
Protects young by carrying them in her mouth.
-
Lives up to 45 years in the wild.
Anaconda
-
Largest snake in the world by weight.
-
Can reach 9 meters in length.
-
Weighs up to 250 kilograms.
-
Non-venomous constrictor.
-
Swallows prey whole after squeezing it.
-
Lives in swamps and rivers of South America.
-
Hunts mostly at night.
-
Can eat caimans, deer, and even jaguars.
-
Females give birth to live young.
-
Excellent swimmer, rarely seen on land.
Thank you for reading! Don’t forget to leave a comment about your opinion.
Read More – Crocodile vs Hippopotamus : A Comprehensive Comparison
References
-
Grigg, G. et al. (2007). Biology and Evolution of Crocodylians.
-
Rivas, J.A. (2000). “Natural History of the Green Anaconda.” University of Tennessee.
-
Pooley, A.C. (1982). “The status of crocodile research and conservation in Africa.”





Leave a Reply