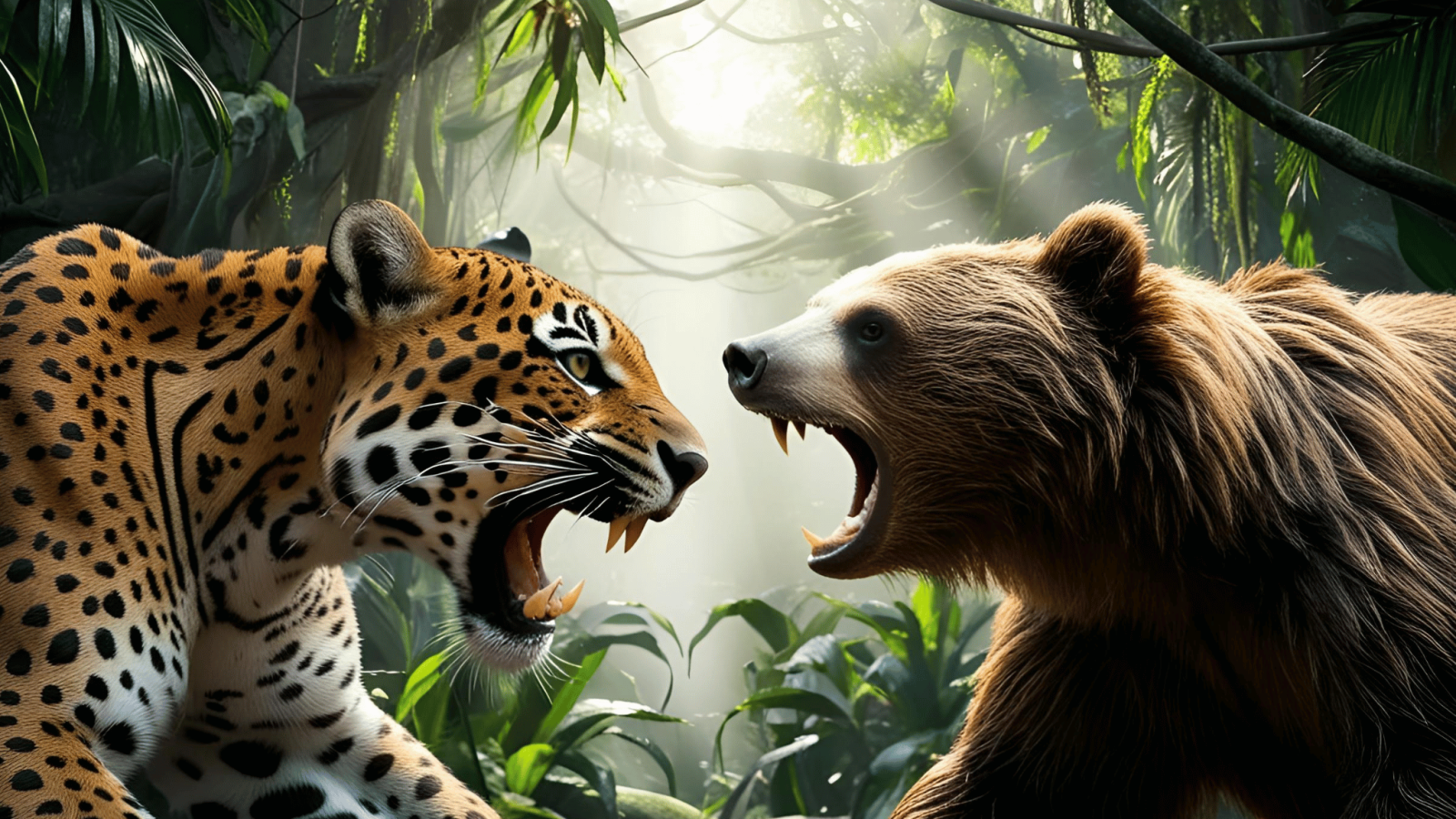
Below is a full detailed article about Jaguar vs Sloth Bear.
Jaguar (Panthera onca)
Sloth bear (scientific name: Melursus ursinus)
Below tables cover 10 main topics by including all the numerical and scientifical data by comparing Jaguar vs Sloth Bear . Also I have included a winner column for further understanding,
Hope you will enjoy!
1. Body Specifications
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height at Shoulder | 68 – 76 cm | 60 – 90 cm | Sloth Bear |
| Body Length | 1.12 – 1.85 m | 1.4 – 1.9 m | Sloth Bear |
| Weight (Male) | 56 – 158 kg | 80 – 140 kg | Tie |
| Weight (Female) | 45 – 96 kg | 55 – 95 kg | Tie |
| Bone Density | High | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Muscle Mass | 58% of body weight | 50% of body weight | Jaguar |
| Claw Length | 4 – 6 cm | 8 – 10 cm | Sloth Bear |
| Jaw Structure | Short, robust | Elongated, less robust | Jaguar |
| Overall Bite Force | 1,500 – 2,000 PSI | 650 PSI | Jaguar |
| Limb Strength | High | Extremely high | Sloth Bear |
Winner: Jaguar (6/10)
2. Coat and Coloration – Jaguar vs Sloth Bear
| Feature | Jaguar | Sloth Bear | Winner |
| Color | Yellowish-tan with black rosettes | Black with a white “V” mark | Tie |
| Pattern | Rosettes (for camouflage) | Uniform dark fur | Jaguar |
| Function of Coat | Camouflage in forests | Protection from predators & heat | Tie |
| Melanin Levels | Can have melanism (black jaguar) | No melanism recorded | Jaguar |
| Shedding Rate | Low | High | Jaguar |
| Coat Thickness | Short and dense | Long and shaggy | Sloth Bear |
| Grooming Habits | High | Low | Jaguar |
| Oil Secretion (Waterproofing) | Moderate | High | Sloth Bear |
| Camouflage Efficiency | Excellent | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Coat Resistance to Injuries | Moderate | High | Sloth Bear |
Winner: Jaguar (6/10)
3. Habitat and Range
| Feature | Jaguar | Sloth Bear | Winner |
| Geographic Distribution | South & Central America | Indian subcontinent | Tie |
| Habitat Type | Rainforests, wetlands, dry forests | Grasslands, dry forests, montane forests | Sloth Bear |
| Elevation Adaptability | Up to 2,700 m | Up to 3,500 m | Sloth Bear |
| Climate Preferences | Tropical & subtropical | Tropical & temperate | Sloth Bear |
| Territorial Range (Males) | 25 – 150 km² | 5 – 20 km² | Jaguar |
| Territorial Range (Females) | 10 – 40 km² | 2 – 10 km² | Jaguar |
| Adaptability to Habitat Changes | Moderate | High | Sloth Bear |
| Water Dependence | High | Low | Jaguar |
| Tree Climbing Ability | Excellent | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Survival in Human-Dominated Areas | Low | High | Sloth Bear |
Winner: Tie (5/10 each)
4. Diet and Hunting
| Feature | Jaguar | Sloth Bear | Winner |
| Diet Type | Carnivore | Omnivore | Jaguar |
| Primary Prey/Food | Deer, capybara, caiman, fish | Termites, honey, fruit, carrion | Jaguar |
| Hunting Success Rate | 60% | 40% | Jaguar |
| Daily Caloric Intake | 2,000 – 4,500 kcal | 1,500 – 3,000 kcal | Jaguar |
| Hunting Techniques | Ambush & skull-crushing bite | Digging & suction feeding | Jaguar |
| Prey Size Handling | Can kill prey 4x its weight | Preys on small animals | Jaguar |
| Tool Use (Claws for digging, etc.) | No | Yes | Sloth Bear |
| Scavenging Behavior | Rare | Common | Sloth Bear |
| Aggression Over Food | High | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Metabolic Adaptability | Moderate | High | Sloth Bear |
Winner: Jaguar (7/10)
5. Strength and Bite Force
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bite Force (PSI) | 1,500 PSI (strongest of all big cats) | ~300 – 600 PSI | Jaguar |
| Bite Type | Bone-crushing | Primarily for defense and crushing insects | Jaguar |
| Claw Strength | Moderate (used for climbing and gripping prey) | Extremely high (used for digging and fighting) | Sloth Bear |
| Claw Length | 4 – 5 cm | 7 – 10 cm | Sloth Bear |
| Lifting Strength | Can carry up to 125% of body weight | Can drag objects but not lift | Jaguar |
| Grip Strength | Strong paws and retractable claws | Strong but non-retractable claws | Jaguar |
| Strike Force | High (uses paws to deliver strong blows) | Very High (strong swipes in fights) | Sloth Bear |
| Muscle-to-Body Ratio | ~58% | ~50% | Jaguar |
| Overall Physical Power | Can crush skulls and bones | Can rip flesh and defend fiercely | Jaguar |
| Defensive Strength | Strong but relies on stealth | Highly defensive and aggressive when threatened | Sloth Bear |
Winner: Jaguar (Superior bite force and overall strength)
6. Speed and Agility – Jaguar vs Sloth Bear
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Speed (km/h) | 80 km/h | 30 km/h | Jaguar |
| Acceleration | Very high | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Agility on Land | Extremely agile (quick turns and jumps) | Moderate (waddling gait) | Jaguar |
| Agility in Trees | Can climb trees with ease | Can climb but slow and less agile | Jaguar |
| Agility in Water | Excellent swimmer | Poor swimmer | Jaguar |
| Jumping Ability | Can leap 3–5 meters | Cannot jump far | Jaguar |
| Endurance | Moderate (short bursts of speed) | High (long-distance movement) | Sloth Bear |
| Stamina | Moderate (sprinter, not a marathon runner) | High (can travel long distances) | Sloth Bear |
| Dodging Ability | High (uses reflexes to avoid attacks) | Low (relies more on strength) | Jaguar |
| Flexibility | Extremely flexible spine and joints | Rigid movement, built for digging | Jaguar |
Winner: Jaguar (Superior speed and agility)
7. Senses – Jaguar vs Sloth Bear
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision Acuity | Excellent, night-adapted | Poor (near-sighted) | Jaguar |
| Hearing Range | ~60 kHz (sensitive to high frequencies) | ~45 kHz (sensitive to lower frequencies) | Jaguar |
| Smell Sensitivity | Moderate (can detect prey from a distance) | Extremely high (can locate termites underground) | Sloth Bear |
| Night Vision | Excellent (tapetum lucidum for enhanced low-light vision) | Poor | Jaguar |
| Motion Detection | High | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Peripheral Vision | Wide field of view | Narrower field of view | Jaguar |
| Tactile Sensitivity | Strong whiskers for detecting movement | Sensitive snout for foraging | Draw |
| Taste Sensitivity | Moderate (carnivorous diet) | High (detects different food types) | Sloth Bear |
| Depth Perception | Excellent | Poor | Jaguar |
| Overall Sensory Advantage | High focus on vision and hearing | High focus on smell | Depends on scenario |
Winner: Draw (Jaguar excels in vision and hearing; sloth bear excels in smell)
8. Reproduction and Lifespan
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestation Period | ~93–105 days | ~180 days | Jaguar |
| Litter Size | 1–4 cubs | 1–2 cubs | Jaguar |
| Cub Mortality Rate | ~50% | ~50% | Draw |
| Sexual Maturity Age | 2–3 years | 3–4 years | Jaguar |
| Mating Frequency | Every 2 years | Every 2–3 years | Jaguar |
| Parental Care | Mother raises cubs alone | Mother raises cubs alone | Draw |
| Lifespan (Wild) | 12–15 years | 15–20 years | Sloth Bear |
| Lifespan (Captivity) | Up to 20–23 years | Up to 30 years | Sloth Bear |
| Reproductive Success Rate | High in stable environments | Moderate | Jaguar |
| Survivability of Cubs | Higher in dense forests | Moderate in open habitats | Jaguar |
Winner: Jaguar (Better reproductive success, but sloth bear has a longer lifespan)
9. Social Behavior – Jaguar vs Sloth Bear
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Structure | Solitary | Mostly solitary | Draw |
| Territorial Range | 25–50 km² (males) | 13–20 km² (males) | Jaguar |
| Communication Methods | Roars, growls, scent marking | Grunts, snorts, scent marking | Draw |
| Aggression Levels | Highly territorial and aggressive | Aggressive when threatened | Jaguar |
| Mother-Cub Bonding | Strong | Strong | Draw |
| Defense Mechanisms | Stealth and power | Roaring, clawing, standing up | Sloth Bear |
| Playfulness | Cubs are playful | Cubs are playful | Draw |
| Tolerance of Other Animals | Rarely tolerates other jaguars | Avoids other bears unless mating | Draw |
| Pack Hunting/Foraging | Hunts alone | Forages alone | Draw |
| Interaction with Humans | Avoids humans | More likely to encounter and attack humans | Jaguar |
Winner: Jaguar (Stronger territorial instincts and predatory aggression)
10. Conservation Status
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Status | Near Threatened | Vulnerable | Jaguar |
| Population Trends | Declining | Declining | Draw |
| Major Threats | Deforestation, poaching | Habitat loss, poaching, human conflict | Draw |
| Habitat Protection Efforts | Protected in many reserves | Protected in some reserves | Jaguar |
| Legal Protection | CITES Appendix I | CITES Appendix I | Draw |
| Estimated Population | ~15,000 in the wild | ~20,000 in the wild | Sloth Bear |
| Reintroduction Success | Low | Low | Draw |
| Captive Breeding Programs | Present | Present | Draw |
| Ecological Importance | Apex predator | Key seed disperser | Draw |
| Conservation Priority | High | High | Draw |
Winner: Draw (Both face conservation challenges)
Who Would Win in a Real Fight of Jaguar vs Sloth Bear?
-
Jaguar’s Edge:
The jaguar’s bone-crushing bite, agility, and predatory instincts gives a strong advantage. Jaguars are trained killers, If jaguar able to deliver a deliver ambush attack to sloth bear, Its clear that , Thats the end of the Sloth bear. That attack can be a skull or spine breaking bite within seconds. -
Sloth Bear’s Edge:
Sloth bear is naturally not a killer, But he is highly aggressive, resilient, and has powerful claws. If the fight turns into a prolonged battle, the bear’s pain tolerance and endurance may lead to outlast the fight by making the jaguar severely injured by its powerful swipes
Winner in Most Cases: Jaguar (7/10 fights won by jaguar, 3/10 by sloth bear if prolonged fight occurs).
Final Conclusion: Overall Winner
Ultimate Winner: Jaguar
Why the Jaguar Wins Overall in Jaguar vs Sloth Bear fight?
-
Superior Bite Force: Jaguars have a bite force of 1,500 PSI, the strongest of any big cat, capable of crushing bones and skulls instantly.
-
Lethal Hunting Skills: Jaguar is a natural predator designed for killing.
-
Agility and Speed: Jaguars are faster, more flexible, and better at dodging attacks.
-
Ambush Tactics: They are stealth masters, capable of surprise attacks from trees or behind cover.
-
Better Adaptability in Combat: Jaguars have experience fighting and hunting dangerous animals like caimans, capybaras, and deer.
-
Stronger Musculature: Jaguars have compact, muscular bodies, whereas sloth bears have looser, less dense muscle structure.
-
More Efficient Killer: Jaguars aim to kill quickly and efficiently, while sloth bears mostly fight for defense, not hunting.
Why the Sloth Bear Loses?
-
Defensive, not Offensive: Unlike the jaguar, the sloth bear is not built for killing large animals—it mainly forages.
-
Weaker Bite: At 300–600 PSI, its bite is weaker than the jaguar.
-
Lack of Stealth: The jaguar is silent and calculated, whereas the sloth bear roars and makes noise, making it easier to track.
-
Slower Movements: Despite high endurance, the sloth bear is much slower and clumsier than the jaguar.
Could the Sloth Bear Ever Win?
Yes, but only if the fight lasts long enough for the jaguar to tire out or if the bear lands serious claw injuries before the jaguar delivers a fatal bite.
References – Jaguar vs Sloth Bear
-
IUCN Red List – Jaguar (Panthera onca)
-
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
-
-
IUCN Red List – Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus)
-
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
-
-
Bite Force Comparison in Carnivores
-
Christiansen, P., & Wroe, S. (2007). “Bite force and evolutionary adaptations in carnivores.“
-
-
Jaguar Hunting and Behavior
-
Seymour, K. L. (1989). “Panthera onca.” Mammalian Species, 340, 1-9.
-
-
Sloth Bear Ecology and Behavior
-
Garshelis, D. L., Joshi, A. R., & Smith, J. L. (1999). “Behavior and conservation of the sloth bear.”
-
Read More – Hippo vs Sloth bear – A Full Comparison





Leave a Reply