What if the aggressive muscular, fast bull attacks the largest and strongest animal in the wild? bull vs elephant , Sounds interesting right? In this fully detailed article we are going to analyze these two heavy weight herbivores with their unique features and specifications.
- Bull (Bos taurus)
- Elephant (Loxodonta/Elephas)
Its wonderful that how mother nature designed them. We are just gonna review those designs. Actually, Can a bull stand a chance against an elephant with its sharp horns? Will it be deadly for the elephant If bull heavily attacks the elephant? Lets find out! Keep reading till the end. We are pretty sure that you will be able to learn many new facts. Enjoy!
1. Body Specifications
| Subtopic | Bull (Bos taurus) | Elephant (Loxodonta/Elephas) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height at Shoulder | 1.4 – 1.8 meters | 2.5 – 4 meters | Elephant |
| Body Length | 2.4 – 3 meters | 5.5 – 7.5 meters | Elephant |
| Weight | 800 – 1,100 kg | 2,700 – 6,000+ kg | Elephant |
| Body Shape | Stocky, muscular | Massive, columnar, rounded | Elephant |
| Bone Density | High | Extremely high | Elephant |
| Muscle Mass | Heavy-set, particularly in shoulders | Exceptionally muscular, especially trunk & legs | Elephant |
| Skull Thickness | Thick | Extremely thick with reinforced cranial dome | Elephant |
| Neck Strength | Strong | Strong and fused with skull | Elephant |
| Center of Gravity | Low | Very low | Draw |
| Horns/Tusks | Curved horns (50–80 cm) | Long tusks (up to 3 meters in males) | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (9/10)
2. Coat and Coloration – Bull vs Elephant
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Color | Brown, black, white, mottled | Gray, brownish-gray | Bull |
| Pattern | Some breeds have patterns | Uniform coloration | Bull |
| Coat Thickness | Thick, varies by breed | Very sparse hair | Bull |
| Seasonal Molt | Somewhat seasonal | Minimal molting | Bull |
| Function of Coat | Protection and temperature regulation | Minor — mostly for touch sensitivity | Bull |
| Skin Thickness | Moderate (~6 mm) | Very thick (~2.5–4 cm) | Elephant |
| Camouflage | Poor | Moderate in dusty or muddy environments | Elephant |
| Melanism/Albinism | Rare in some breeds | Extremely rare | Bull |
| Thermoregulation | Via sweat and panting | Uses ears and mud baths | Elephant |
| Skin Maintenance | Low grooming needs | Dusting, bathing, wallowing | Elephant |
Category Winner: Bull (6/10)
3. Habitat and Range
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Habitat | Farms, plains, domesticated lands | Forests, savannas, grasslands | Elephant |
| Geographic Range | Worldwide (domestic) | Sub-Saharan Africa, South and Southeast Asia | Elephant |
| Terrain Adaptability | Grasslands, farms | Forests, rivers, grasslands, hills | Elephant |
| Climate Tolerance | High (cold and warm breeds) | Tropical and subtropical | Bull |
| Elevation Range | Sea level to 3,000+ meters | Sea level to 3,500+ meters | Elephant |
| Shelter Preferences | Barns, trees | Forest canopy, caves, shade | Elephant |
| Range Size | Limited to farmland | Ranges up to 1,000 sq. km | Elephant |
| Migration Behavior | None | Seasonal migratory routes | Elephant |
| Wild Survival | Very low without humans | Fully wild and independent | Elephant |
| Population Influence | Bred and maintained by humans | Declining in wild, but ecologically critical | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (9/10)
4. Diet and Feeding Behavior
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diet Type | Herbivore | Herbivore | Draw |
| Daily Intake | 9–12 kg of dry matter | 150–200 kg of vegetation | Elephant |
| Digestive System | Ruminant (4-chambered stomach) | Hindgut fermenter | Bull |
| Feeding Time per Day | 6–8 hours | 14–18 hours | Elephant |
| Water Consumption | 30–50 liters/day | 100–200 liters/day | Elephant |
| Preferred Food | Grasses, hay, silage | Bark, leaves, grass, fruits | Elephant |
| Foraging Technique | Grazes with mouth | Uses trunk for plucking and stripping trees | Elephant |
| Food Storage | None | None | Draw |
| Efficiency | High due to domesticated diet | Lower — needs more volume | Bull |
| Feeding Tools | Lips, tongue, jaw | Trunk and tusks | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (6/10)
5. Strength and Power – Bull vs Elephant
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pushing Force | 1,000–1,500 kg | Over 6,000 kg (entire body weight) | Elephant |
| Lifting Capability | Minimal (not designed for lifting) | Can lift 300+ kg with trunk | Elephant |
| Kick Force | Powerful hind leg kick | Can crush with feet | Elephant |
| Body Slam Force | Very high due to mass and speed | Devastating due to size and momentum | Elephant |
| Charge Speed | 40–50 km/h | 25–40 km/h | Bull |
| Crushing Ability | Medium (hooves) | Extreme (foot and weight) | Elephant |
| Skull Strength | Thick, curved skull | Massive frontal bone and dome | Elephant |
| Trunk Force | None | Can uproot small trees | Elephant |
| Tail as Weapon | Not effective | Used for communication, not combat | Draw |
| Defensive Power | Horns for goring | Tusks and sheer mass | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (8/10)
6. Speed and Agility
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Speed | 40–50 km/h | 25–40 km/h | Bull |
| Acceleration | Fast in short bursts | Slow starter | Bull |
| Turning Radius | Moderate | Wide turning due to size | Bull |
| Jumping Ability | Can hop short distances | Cannot jump | Bull |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Very limited | Bull |
| Balance | Stable on hooves | Extremely stable due to size | Draw |
| Agility on Uneven Ground | Moderate | Surprisingly agile for size | Elephant |
| Obstacle Navigation | Moderate | Good (uses trunk for terrain) | Elephant |
| Energy Efficiency | High for short bursts | High for long distances | Elephant |
| Stamina | High (domesticated) | Very high (long travel ranges) | Elephant |
Category Winner: Bull (5/10)
7. Senses and Awareness
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision | Moderate (wide field) | Good, with excellent peripheral vision | Elephant |
| Hearing | Sharp | Extremely sensitive (low-frequency sounds) | Elephant |
| Smell | Strong | Exceptional (one of the best in mammals) | Elephant |
| Touch Sensitivity | Moderate | Extremely high in trunk and skin | Elephant |
| Communication | Limited (grunts, bellowing) | Vocalizations, infrasound, body language | Elephant |
| Awareness of Threats | High (prey instincts) | Very high | Elephant |
| Night Vision | Poor | Moderate | Elephant |
| Tactile Organs | Nose and lips | Trunk, feet, tail | Elephant |
| Cognitive Mapping | None | Excellent memory of territory and routes | Elephant |
| Emotional Sensing | Low | Very high — shows empathy and mourning | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (10/10)
8. Intelligence and Learning
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Problem Solving | Very low | Advanced | Elephant |
| Memory | Short-term memory | Excellent long-term memory | Elephant |
| Social Learning | Minimal | Observational and experiential learning | Elephant |
| Tool Use | None | Frequently uses trunk and objects | Elephant |
| Communication Skills | Basic | Complex vocal and tactile language | Elephant |
| Planning Ability | None | Shown in travel and defense strategies | Elephant |
| Cooperation | None | Coordinated in groups | Elephant |
| Awareness | Basic | High self-awareness (mirror test passed) | Elephant |
| Adaptability | Medium (as livestock) | Very high | Elephant |
| Emotional Complexity | Low | Very high | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (10/10)
9. Social Behavior – Bull vs Elephant
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Structure | Solitary or small herd | Highly social, matriarchal herds | Elephant |
| Group Cooperation | Minimal | Extensive coordination | Elephant |
| Aggression Display | High (territorial) | Controlled aggression | Bull |
| Parental Care | None | Strong maternal and allomothering behavior | Elephant |
| Social Bonding | Weak | Strong and lasting | Elephant |
| Communication Style | Basic sounds | Complex calls, body movement, infrasound | Elephant |
| Hierarchy | Based on size and age | Matriarchal leadership | Elephant |
| Conflict Resolution | Fight-based | Often non-violent, uses posture | Elephant |
| Interaction Frequency | Rare | Constant in herds | Elephant |
| Reproduction Sociality | Aggressive during mating | Subtle rituals and protection | Elephant |
Category Winner: Elephant (9/10)
10. Conservation and Human Interaction
| Subtopic | Bull | Elephant | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Status | Not listed (domesticated) | Endangered/Vulnerable | Bull |
| Human Dependency | Total (farm animals) | None in wild | Elephant |
| Wild Population | Not applicable | ~400,000 (African), <50,000 (Asian) | Bull |
| Habitat Threat | None (domesticated) | High due to deforestation | Bull |
| Use in Culture | Meat, labor, sports | Symbol of wisdom, religious significance | Elephant |
| Ethical Debates | Bullfighting, livestock treatment | Captivity, ivory trade | Draw |
| Conservation Efforts | Minimal (not needed) | Intense international focus | Elephant |
| Danger to Humans | Medium (accidents, rage) | High (territorial defense) | Draw |
| Legal Protections | Basic livestock laws | Strict CITES and wildlife laws | Elephant |
| Future Outlook | Stable population | Threatened by habitat loss and poaching | Bull |
Category Winner: Elephant (5/10)
Find More – Bull Battles
Find More – Elephant Battles
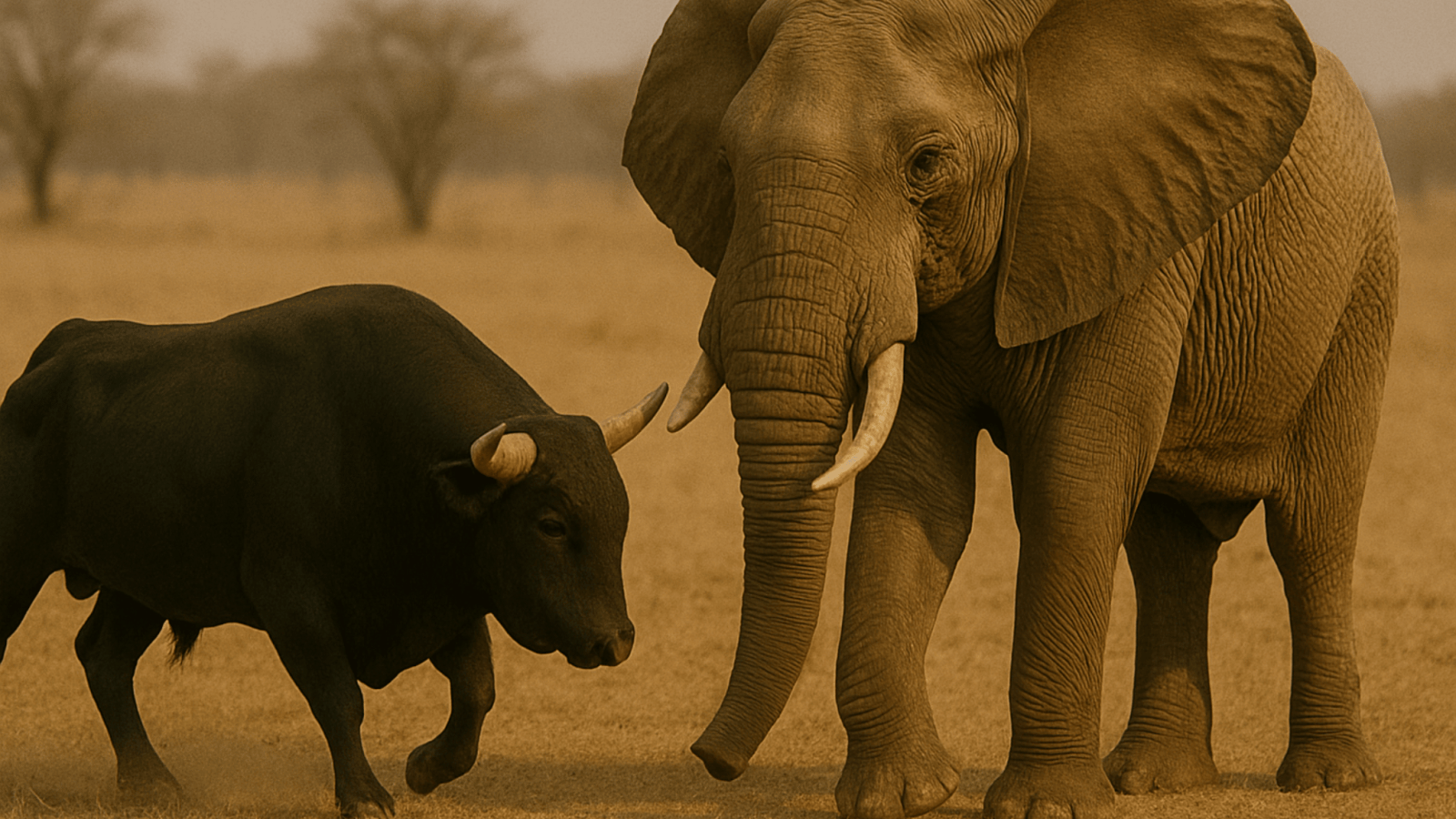
⚔️ Face-to-Face Fight: Bull vs Elephant
In a real fight, the bull may fight more aggressively, using its horns, speed, and brute strength. But the elephant who is weighing several more tons than the bull, has overwhelming physical superiority, reinforced by tusks, a powerful trunk, and an unshakable center of gravity.
- If the bull attacks, the elephant can absorb the damage also and with the elephants long tusks and massive legs one attack will be fatal to the bull
- Due to elephant heavy size Its not easy for the bull to attack. Even attack with the horns. Mostly has do it to the Legs.
Even the elephant is being extremely young or sick, the bull has no realistic chance of winning in a face to face battle.
Final Winner: Elephant
| Total Categories Won | Elephant: 9 | Bull: 1 |
|---|
✅ Why the Elephant Wins:
- Overwhelming Size and Weight: Several times larger, elephants are the biggest.
- Superior Weaponry: Tusks, trunk strikes, and stomps are deadly in close combat.
- Higher Intelligence: Allows for better strategic decisions in conflict.
- Better Endurance: Elephants can fight longer and harder without fatigue.
- Stability: Massive legs and wide base make elephants nearly impossible to defeat.
❌ Why the Bull Loses:
- Smaller Size: Too small.
- Limited Offensive Tools: Horns are useless against such thick skin.
- Lack of Combat Strategy: Bulls fight with anger and not with tactics.
- Poor Durability Against Tusks: A single tusk attack could cause severe damage.
Conclusion: Bull vs Elephant Who Wins?
Even the bull is tough, aggressive and strong it simply cannot defeat a fully grown elephant. So in this epic battle bull vs elephant, elephant has a clear win with massive advantages. If you’re wondering “bull vs elephant who wins,” the answer is already very clear: the elephant wins due to strength, intelligence, and natural weaponry.
Interesting Facts About Bulls
- Bulls can weigh over 1,000 kg, depending on the type, their muscles are built for pushing and pulling.
- They cannot see red —They are always getting triggered when see red
- Bulls are normally so aggressive
- They have caused more human injuries than most large wild animals.
- Some bulls are used in cultural sports, like Spanish bullfighting and Indian Jallikattu.
Interesting Facts About Elephants
- Elephants are the largest land mammals, with African males reaching up to 6,000+ kg.
- Their trunks have over 40,000 muscles and can delicately pick up a peanut or uproot a tree.
- Elephants are known to mourn their dead, showing advanced emotional intelligence.
- Their ears help regulate body temperature by dissipating heat through large surface areas.
- An elephant’s tusk continues growing for life, and it’s actually an elongated incisor tooth.
References – Bull vs Elephant
- National Geographic. (n.d.). African Elephant Facts. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/african-elephant
- Britannica. (n.d.). Elephant | Mammal. https://www.britannica.com/animal/elephant-mammal
- FAO. (2023). Livestock Production – Cattle. https://www.fao.org/livestock/cattle
- WWF. (n.d.). Elephants | Species. https://www.worldwildlife.org/species/elephant
- Animal Diversity Web. (n.d.). Bos taurus (Bull). https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Bos_taurus





Leave a Reply