Below is a full detailed article about Black Panther vs Cheetah?
Cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus)
Black panther (Panthera pardus or Panthera onca, depending on region)
Below tables cover 10 main topics by including all the numerical and scientifical data by comparing Black Panther vs Cheetah. Also I have included a winner column for further understanding,
Hope you will enjoy!
1. Body Specifications
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height at Shoulder | 60–70 cm | 67–94 cm | Cheetah |
| Body Length (head-body) | 1.0–1.9 m | 1.1–1.5 m | Tie |
| Weight | 30–90 kg | 21–72 kg | Black Panther |
| Muscle Mass | Dense, compact | Lean, optimized for speed | Black Panther |
| Bone Density | High | Moderate | Black Panther |
| Body Shape | Stocky, muscular | Slim, aerodynamic | Tie |
| Tail Length | 60–110 cm | 60–80 cm | Black Panther |
| Neck Thickness | Thick | Thin | Black Panther |
| Skull Strength | Strong | Light | Black Panther |
| Claw Size | ~4 cm | ~3.5 cm | Black Panther |
Winner: Black Panther — Stronger and more powerful physique.
2. Coat and Coloration
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fur Color | Black (melanistic) | Yellow-golden with black spots | Tie |
| Pattern | Rosettes (hidden under black coat) | Solid black spots | Cheetah |
| Camouflage Function | Excellent in forests | Excellent in savannas | Tie |
| Melanin Levels | High (melanism) | Normal | Black Panther |
| UV Reflection | Low (stealthy) | Moderate | Black Panther |
| Thermal Regulation | Good in shade | Optimized for sun | Cheetah |
| Hair Texture | Dense | Fine | Black Panther |
| Facial Markings | Hard to distinguish | Black tear marks (sun glare reduction) | Cheetah |
| Color Variation | Rare (melanistic) | Rare (king cheetah) | Tie |
| Stealth Factor | Very high in jungle | High in open terrain | Black Panther |
Winner: Black Panther — Superior for stealth and forest hunting.
3. Habitat and Range
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Habitat | Rainforests, woodlands | Grasslands, savannas | Tie |
| Geographic Range | Africa, SE Asia | Sub-Saharan Africa, Iran | Tie |
| Elevation Tolerance | Up to 2,600 m | Up to 2,000 m | Black Panther |
| Habitat Flexibility | Very high | Moderate | Black Panther |
| Territory Size | 10–60 km² | 20–200 km² | Cheetah |
| Shelter Use | Trees, caves, dense brush | Tall grass, open plains | Tie |
| Climate Tolerance | Humid, warm, temperate | Arid to warm | Tie |
| Nocturnal Activity | Predominantly nocturnal | Diurnal | Black Panther |
| Adaptability to Humans | High | Low | Black Panther |
| Range Shrinkage | Severe | Very severe | Tie |
Winner: Black Panther — More versatile and better adapted to diverse habitats.
4. Diet and Hunting – Black Panther vs Cheetah
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diet Type | Carnivore | Carnivore | Tie |
| Prey Size Range | Small to medium (30–80 kg) | Small to medium (10–40 kg) | Black Panther |
| Hunting Strategy | Ambush from above or stealth | Chase and trip | Tie |
| Success Rate | 30–40% | 50–60% | Cheetah |
| Kill Method | Neck bite/suffocation | Throat clamp | Tie |
| Bite Force | ~310 PSI | ~475 PSI | Cheetah |
| Hunting Time | Night | Day | Tie |
| Caloric Intake Daily | ~3,000–4,000 kcal | ~2,500–3,000 kcal | Black Panther |
| Kill Storage | Caches in trees | None | Black Panther |
| Solo Hunting | Yes | Yes | Tie |
Winner: Black Panther — Broader prey range and caching behavior provide survival edge.
5. Strength and Bite Force
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bite Force | ~310 PSI | ~475 PSI | Cheetah |
| Claw Retraction | Fully retractable | Semi-retractable | Black Panther |
| Climbing Strength | Excellent | Poor | Black Panther |
| Paw Swipe Force | Moderate | Low | Black Panther |
| Muscle Density | High | Low | Black Panther |
| Lifting Power | Can drag prey twice its weight up trees | Limited | Black Panther |
| Grip Strength | High | Low | Black Panther |
| Wrestling Ability | Moderate | Weak | Black Panther |
| Durability in Combat | High | Fragile | Black Panther |
| Killing Efficiency | Moderate | Fast but vulnerable after kill | Tie |
Winner: Black Panther — Stronger overall and more durable.
Awesome! Let’s continue the Black Panther vs Cheetah blog with the remaining categories, the fight breakdown, and the final verdict.
6. Speed and Agility – Black Panther vs Cheetah
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Speed | ~58 km/h | ~112 km/h | Cheetah |
| Acceleration (0–60 km/h) | ~3.5 seconds | ~2.5 seconds | Cheetah |
| Agility (Land) | High | Extremely High | Cheetah |
| Turning Radius | Tight | Ultra-tight (tail-assisted) | Cheetah |
| Tree Navigation | Excellent | Poor | Black Panther |
| Balance (Tail Use) | Good | Excellent | Cheetah |
| Stamina | Moderate | Very low (sprint only) | Black Panther |
| Jump Length | Up to 6 m | Up to 7 m | Cheetah |
| Water Agility | Poor | Poor | Tie |
| Escape Maneuvering | Good | Exceptional | Cheetah |
Winner: Cheetah — The fastest land animal easily dominates in speed and maneuverability.
7. Senses – Black Panther vs Cheetah
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision (Day) | Good | Excellent | Cheetah |
| Vision (Night) | Excellent | Moderate | Black Panther |
| Hearing Range | Up to 60 kHz | Up to 60 kHz | Tie |
| Olfactory Senses | Strong | Strong | Tie |
| Whisker Sensitivity | High | High | Tie |
| Color Vision | Limited | Moderate | Tie |
| Facial Tear Mark Use | Absent | Reduces glare | Cheetah |
| Environmental Awareness | High | High | Tie |
| Sensory Integration | Balanced | Speed-optimized | Black Panther |
| Stealth Hearing Utilization | High | Moderate | Black Panther |
Winner: Tie — Each has evolved senses suited to different lifestyles (nocturnal ambusher vs diurnal sprinter).
8. Reproduction and Lifespan
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestation Period | ~90–105 days | ~90–95 days | Tie |
| Litter Size | 2–4 cubs | 3–5 cubs | Cheetah |
| Cub Mortality Rate | ~50% | Up to 90% | Black Panther |
| Sexual Maturity (Female) | ~2.5 years | ~2 years | Cheetah |
| Sexual Maturity (Male) | ~3 years | ~2.5 years | Cheetah |
| Parental Care | Solitary mother | Solitary mother | Tie |
| Weaning Age | ~3 months | ~3 months | Tie |
| Lifespan (Wild) | 12–17 years | 10–12 years | Black Panther |
| Lifespan (Captivity) | 20+ years | ~17 years | Black Panther |
| Reproductive Frequency | Every 2 years | Every 1.5–2 years | Cheetah |
Winner: Black Panther — Lower cub mortality and longer lifespan.
9. Social Behavior
| Feature | Black Panther | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Structure | Solitary | Mostly solitary, males may form coalitions | Tie |
| Territorial Marking | Scent, scratches | Scent, visual | Tie |
| Territory Size | Smaller | Larger | Cheetah |
| Conflict Avoidance | High | Very high | Tie |
| Parent-Offspring Bond | Strong (short term) | Strong | Tie |
| Male-Male Interaction | Rare | Coalition possible | Cheetah |
| Vocalizations | Roars, growls, chuffs | Chirps, purrs, meows | Tie |
| Territorial Aggression | Moderate | Low | Black Panther |
| Mating Behavior | Brief and aggressive | Brief and cautious | Tie |
| Tolerance of Humans | High (urban-adapted) | Low | Black Panther |
Winner: Tie — Both cats are mostly solitary and show different adaptations.
10. Conservation Status
| Feature | Black Panther (Leopard, melanistic) | Cheetah | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Status | Vulnerable | Vulnerable | Tie |
| Wild Population Estimate | ~700,000 leopards (melanistic rare) | ~7,100 | Black Panther |
| Main Threats | Habitat loss, poaching | Habitat loss, inbreeding, human conflict | Tie |
| Conservation Programs | Widespread | Intensive breeding programs | Tie |
| Range Fragmentation | Moderate | Severe | Black Panther |
| Habitat Adaptability | High | Low | Black Panther |
| Genetic Diversity | Moderate | Low | Black Panther |
| Captive Viability | Good | Low success | Black Panther |
| Illegal Trade Impact | High | High | Tie |
| Human Conflict | Moderate | High | Black Panther |
Winner: Black Panther — More resilient and adaptable species.
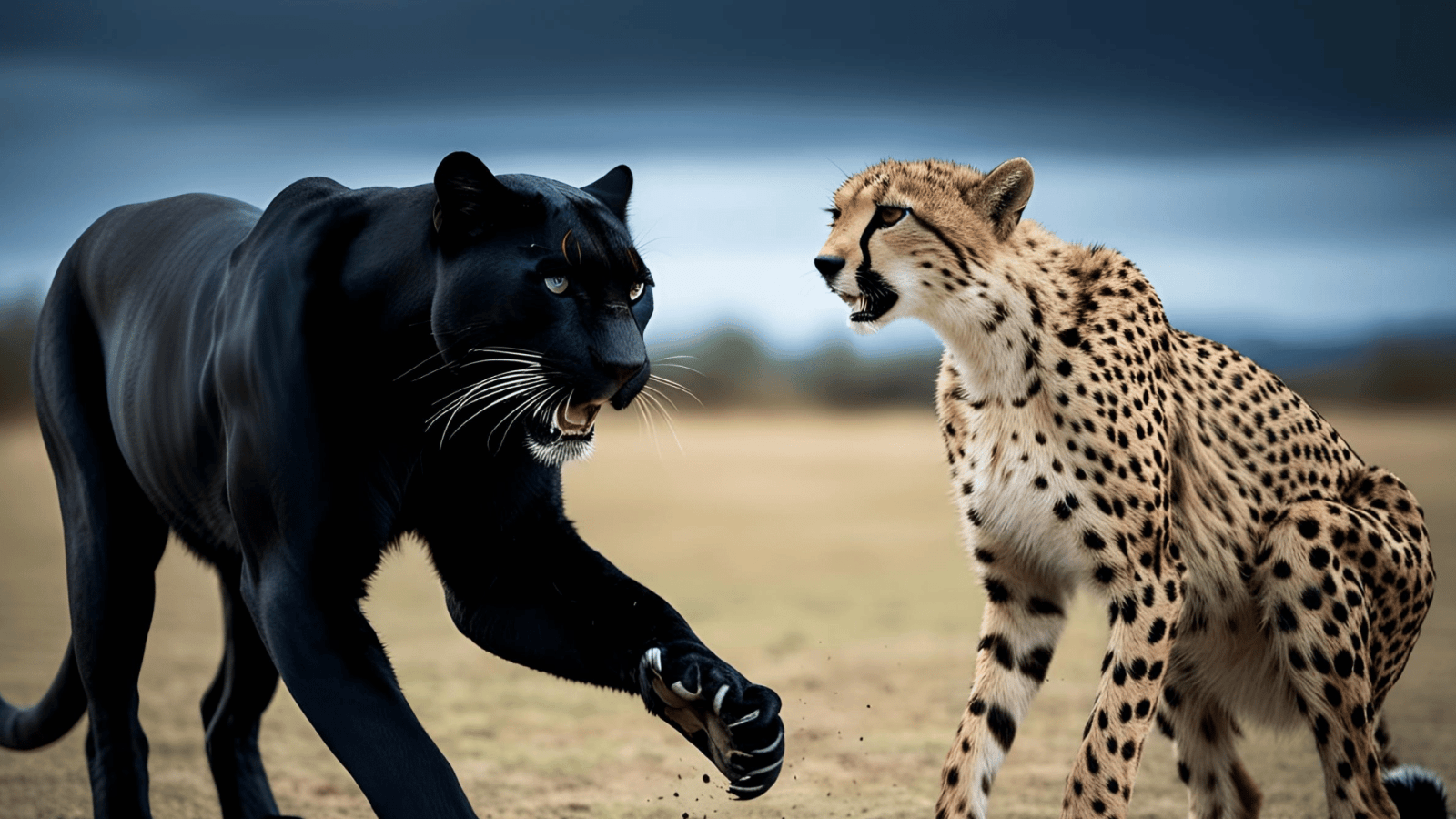
⚔️ Face-to-Face Fight: Who Would Win?
In a direct physical fight,
the black panther—a muscular, stealthy predator with strong jaws, retractable claws, and tree-climbing prowess—plays a main combat advantage over the cheetah, which is built for speed, not combat.
Fight Breakdown:
- First strike advantage: Likely goes to the black panther due to ambush behavior.
- Strength and durability: Black panther vastly outmatches the cheetah.
- Escape potential: Cheetah might escape in open ground but risks fatal injury in any engagement.
- Combat instinct: Panther is a more aggressive and powerful fighter.
✅ Face-to-Face Winner: Black Panther
Final Verdict: Black Panther vs Cheetah?
| Category | Winner |
|---|---|
| Body Specifications | Black Panther |
| Coat and Coloration | Black Panther |
| Habitat and Range | Black Panther |
| Diet and Hunting | Black Panther |
| Strength and Bite Force | Black Panther |
| Speed and Agility | Cheetah |
| Senses | Tie |
| Reproduction & Lifespan | Black Panther |
| Social Behavior | Tie |
| Conservation Status | Black Panther |
✅ Final Score: Black Panther – 7 | Cheetah – 1 | Tie – 2
Why Black Panther Wins
- Superior strength, endurance, and killing ability
- Exceptional stealth and adaptability
- More durable in a physical encounter
- Survivability in varied environments
Why Cheetah Loses
- Physically fragile and vulnerable in combat
- Built for speed, not for defense or strength
- Poor tree-climbing, low endurance, and non-aggressive behavior
References
- Panthera.org – Leopard Conservation
- IUCN Red List – Panthera pardus
- IUCN Red List – Acinonyx jubatus
- National Geographic – Cheetah Facts
- BBC Earth – The Secret Life of Black Panthers
Read More – Black Panther vs Hyena : Brutal Sci-fi Comparison





Leave a Reply