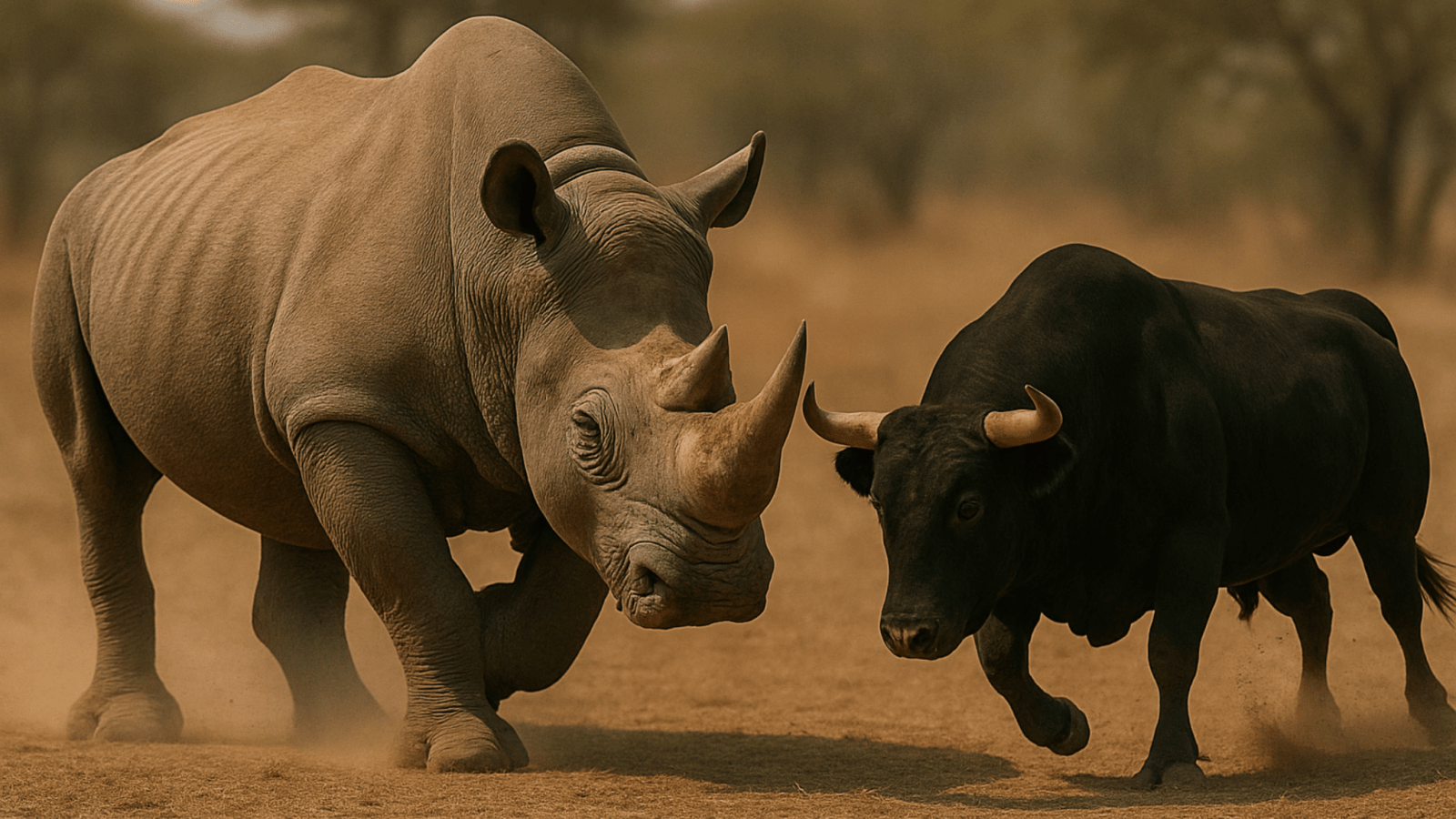
Have you ever imagine a bull vs rhino fight, Anyway it’s easy to imagine two big creatures sizing each other up like heavyweight wrestlers. But let’s look at this matchup with a curious eye instead of a dramatic one like Kungfu panda. Here we are gonna talk according to the features that mother nature gave.
On one side, we have the bull—strong, stubborn. On the other, the rhino a gentle looking natural tank with a horn, thick skin, and a surprisingly chill attitude (most of the time). Both of them are herbivores, love their personal space, and aren’t exactly built for stealth. Anyway what would be happen if they cross paths and engaged to a face to face Bull vs Rhino fight? Let’s dive into this interesting direct fight and see how these two giants battles in strength, behavior, and personality.
1. Body Specifications
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Bos taurus | Rhinocerotidae (various species) | Rhino |
| Average Weight | 700–1,100 kg | 1,800–2,700 kg (White Rhino), 800–1,400 kg (Indian Rhino) | Rhino |
| Height at Shoulder | 1.5–1.8 meters | 1.6–2 meters | Rhino |
| Body Length | 2.0–2.5 meters | 3.0–4.0 meters | Rhino |
| Body Shape | Muscular, barrel-chested | Stocky, tank-like with a broad chest | Rhino |
| Horn Structure | 2 keratin horns; up to 30 cm | 1–2 keratin horns; longest recorded 150+ cm | Rhino |
| Bone Density | High | Extremely high – supports massive weight | Rhino |
| Muscle Mass | Up to 40% of body weight | Extremely muscular, especially neck and shoulders | Draw |
| Skin Thickness | ~6 mm | 25–50 mm in some areas (dermal armor) | Rhino |
| Combat Durability | Strong but vulnerable to goring or tearing | Incredibly resistant to injury due to thick hide | Rhino |
Category Winner: Rhino – Superior in size, skin thickness, and body armor.
2. Coat and Coloration
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coat Color | Black, brown, red, or white | Gray, brown, or slate-colored | Draw |
| Coat Thickness | Moderate | Sparse hair, thick skin | Bull |
| Camouflage Ability | Minimal | Blends in with dusty savannah or muddy waterholes | Rhino |
| Skin Functionality | Protection, minor thermoregulation | Armor-like, protects from insects and injuries | Rhino |
| Melanin Content | Varies by breed | Consistent across species | Bull |
| Seasonal Shedding | Yes | No | Bull |
| Parasite Resistance | Medium | High – aided by symbiotic birds | Rhino |
| Dirt-Wallowing Habit | Rare | Frequent – protects from sun and parasites | Rhino |
| Water Retention | Moderate | High – thick skin reduces moisture loss | Rhino |
| Heat Regulation | Uses shade and water | Thick skin and mud baths for cooling | Rhino |
Category Winner: Rhino – Coating and coloration features better suited for wild survival.
3. Habitat and Range
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Range | Domesticated globally | Sub-Saharan Africa, Indian subcontinent | Rhino |
| Habitat Type | Farmland, grassland, pasture | Savannas, floodplains, forests | Rhino |
| Environmental Adaptability | High due to domestication | Moderate – species-specific | Bull |
| Climate Preference | Temperate to tropical | Tropical to semi-arid | Draw |
| Range Size | Small – managed pasture | Up to 25 km² or more | Rhino |
| Altitude Tolerance | Medium | Can live at low and moderate altitudes | Draw |
| Human Interaction | High | Low – typically avoids humans | Bull |
| Shelter Use | Barns or trees | Bushes, shade trees, or mud wallows | Draw |
| Migration Behavior | None – domestic | Some local movements depending on species | Rhino |
| Water Dependency | High | Very high – must drink daily | Draw |
Category Winner: Rhino – Better adapted to survival in challenging, untamed environments.
4. Diet and Feeding Behavior
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diet Type | Herbivore – grazer | Herbivore – grazer/browsers | Draw |
| Daily Food Intake | ~15–20 kg dry matter | ~50–60 kg of vegetation | Rhino |
| Feeding Hours | 8–10 hours/day | 12+ hours/day | Rhino |
| Jaw Strength | Strong molars for grinding | Strong prehensile lips or front teeth | Draw |
| Prehensile Capability | None | Yes – especially black rhinos | Rhino |
| Tooth Structure | Flat molars | Hypsodont teeth – evolved for grinding fibrous plants | Rhino |
| Foraging Technique | Grazing only | Grazing and browsing depending on species | Rhino |
| Competition for Food | Low – farm managed | Medium – wild resource sharing | Bull |
| Water Consumption | 30–50 L/day | Up to 100 L/day | Rhino |
| Nutritional Efficiency | High – optimized diet | Wild, varies by location | Bull |
Category Winner: Rhino – Though both are herbivores, the rhino out-eats and out-forages the bull.
5. Strength and Horn Power
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horn Length | 20–50 cm | 60–150 cm (front horn) | Rhino |
| Horn Composition | Keratin | Keratin | Draw |
| Horn Use | Charging, goring rivals | Defense, offense, digging | Rhino |
| Charge Force (Est.) | 15,000–20,000 N | Up to 35,000 N | Rhino |
| Head Strength | Powerful skull | Massive reinforced skull | Rhino |
| Muscle Torque | Strong neck and shoulder | Exceptionally strong – can flip objects | Rhino |
| Head-to-Head Combat | Effective in cattle fights | Designed for crushing blows | Rhino |
| Neck Power | 500–800 N-m (estimated) | >1,000 N-m (estimated) | Rhino |
| Ground Impact Shock | Moderate | Devastating – especially at speed | Rhino |
| Injury Resistance | Medium | Very high due to thick skin and muscle | Rhino |
Category Winner: Rhino – Far superior in horn power, impact strength, and resistance.
6. Speed and Agility
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Speed | 40–50 km/h | 40–55 km/h (depending on species) | Rhino |
| Acceleration | Moderate | Surprisingly fast for size | Rhino |
| Turning Agility | Good, especially during bullfighting | Poor – wide turning radius | Bull |
| Stamina | High endurance under domestication | Low to moderate – short bursts only | Bull |
| Jumping Ability | Can jump 1–1.5 meters (in some breeds) | Cannot jump | Bull |
| Movement in Terrain | Good on flat surfaces | Excellent in mud, plains, and forests | Rhino |
| Swimming Capability | Limited or poor | Good swimmer (especially Indian rhino) | Rhino |
| Obstacle Navigation | Moderate | Poor – size limits movement | Bull |
| Slippery Ground Traction | Moderate | Good – wide feet and strong legs | Rhino |
| Burst Power | Good for short charges | Extremely powerful burst charge | Rhino |
Category Winner: Rhino – Wins on speed, burst power, and terrain dominance.
7. Senses and Awareness
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision Range | Moderate – colorblind | Poor – limited vision, relies on other senses | Bull |
| Hearing Sensitivity | Good – detects high and low frequencies | Excellent – swiveling ears detect distant sounds | Rhino |
| Smell Accuracy | Very good | Exceptional – primary sense | Rhino |
| Night Vision | Moderate | Poor to moderate | Bull |
| Peripheral Awareness | High – side-placed eyes | High | Draw |
| Sensory Processing | Fast | Fast – instinct-based reaction | Draw |
| Reaction Time | Good | Slightly slower due to size | Bull |
| Memory and Recognition | Strong memory | Strong memory – especially territorial markers | Draw |
| Stress Response | Variable – often aggressive when provoked | Calm unless threatened | Rhino |
| Fight or Flight Tendency | Tends to fight when provoked | Generally chooses fight | Rhino |
Category Winner: Rhino – Slightly more advantage due to acute smell and sound detection.
8. Reproduction and Lifespan
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestation Period | ~280 days | 450–480 days | Bull |
| Offspring per Birth | 1 calf | 1 calf | Draw |
| Reproductive Frequency | High under management | Very low – one calf every 2–3 years | Bull |
| Age of Sexual Maturity | 1–2 years | 5–7 years | Bull |
| Parental Investment | None (males); moderate (females) | High maternal care | Rhino |
| Cub Mortality Rate | Low due to human protection | High in the wild | Bull |
| Lifespan (Wild) | Not applicable | 35–40 years | Rhino |
| Lifespan (Captivity) | 15–20 years | Up to 45–50 years | Rhino |
| Breeding Challenges | Few under control | Significant – endangered species | Bull |
| Population Growth Rate | High | Low | Bull |
Category Winner: Bull – Due to faster reproductive cycle and population growth.
9. Social Behavior
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Structure | Herds or solitary depending on breed | Mostly solitary except mothers and calves | Bull |
| Territorial Behavior | Medium – especially among bulls | Extremely territorial males | Rhino |
| Dominance Hierarchy | Yes – especially in herds | Yes – strong dominance among males | Draw |
| Aggression Level | High, especially in males | High if provoked | Draw |
| Communication Type | Vocal, posturing, and scent marking | Scent marking, vocalizations, body language | Rhino |
| Group Defense Behavior | Possible in herds | Rare – mostly individual | Bull |
| Mating Competition | High – bulls compete fiercely | High – long, violent fights | Rhino |
| Parental Care | Minimal (except cows) | Only females – long care duration | Rhino |
| Conflict Resolution | Through fights or separation | Physical confrontation | Draw |
| Interaction with Other Species | Frequent (humans, livestock) | Minimal – mostly wild species | Bull |
Category Winner: Draw – Each species shows strengths in different behavioral areas.
10. Conservation Status
| Subtopic | Bull | Rhino | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Status | Not evaluated – domestic species | Vulnerable to Critically Endangered (species dependent) | Bull |
| Population Trend | Stable or increasing | Decreasing – due to poaching and habitat loss | Bull |
| Conservation Priority | Low | High | Rhino |
| Human Threat Level | Low – domesticated | High – poached for horn | Bull |
| Habitat Threats | Low – managed environments | High – habitat fragmentation | Bull |
| Captive Breeding | Widely practiced | Limited success, high cost | Bull |
| Legal Protection | General animal welfare laws | Strict international protection (CITES) | Rhino |
| Conservation Efforts | Low needed | High – multiple international initiatives | Rhino |
| Human Conflict Risk | Moderate – mostly farm incidents | High – territorial clashes in human areas | Bull |
| Genetic Diversity | High – numerous breeds | Low – small populations | Bull |
Category Winner: Bull – Due to domesticated safety and stable population.
Face-to-Face Fight Analysis: Bull vs Rhino
| Aspect | Bull | Rhino | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charge Strength | High – but lighter body mass | Devastating – can flip cars and animals | Rhino |
| Defense Capabilities | Strong hide, fast reaction | Thick armor-like skin, massive build | Rhino |
| Kill Potential | High – can gore with horns | Extreme – can kill with a single charge | Rhino |
| Tactical Instincts | Fast and aggressive | Calm but quick to react when threatened | Draw |
| Endurance in Combat | Longer fight stamina | Quick burst efficiency | Bull |
| Fear Response | Aggressive under stress | Fearless and territorial | Rhino |
Interesting Facts – Bull vs Rhino Fight
Bull
-
Bulls are very strong, muscular, and can weigh up to 2,200 pounds.
-
They have thick necks, large bony heads, and strong, curved horns.
-
Bulls are aggressive, especially when challenged or defending their herd.
-
Their horns are used for fighting and protection.
-
Bulls have a hump on their shoulders and curly hair on their neck for extra protection.
-
They are herbivores and eat mostly grass.
-
Bulls have great stamina and can run surprisingly fast for their size.
Rhino
-
Rhinos are huge, with some weighing up to 5,500 pounds—much heavier than bulls.
-
They have thick, tough skin that looks like armor.
-
Rhinos have one or two horns made of keratin (like human hair and nails).
-
They can run up to 40 km/h (25 mph) for short distances.
-
Rhinos love rolling in mud to cool off and protect their skin.
-
They are mostly solitary but sometimes form small groups called a crash.
-
Rhinos have poor eyesight but a great sense of smell and hearing.
-
Their main threat is poaching for their horns, not natural predators.
Winner in a Bull vs Rhino Fight : Rhino
In a direct confrontation, the rhino’s sheer size, armor, and horn strength give it a massive edge. A bull may attempt to challenge, but it would likely be outmatched and overwhelmed by the rhino’s devastating attacks and resilience.
Overall Winner: Rhino
Why the Rhino Wins:
- Size & Strength: Rhinos heavier than bulls, nearly a ton and are built for tank like power and strength.
- Horn Power: Rhino horns can reach over a meter long and cause fatal damage.
- Armor Protection: Thick skin resists goring and cuts.
- Wild Instincts: As wild animals, rhinos are more adaptable and aggressive in true combat scenarios.
Why the Bull Loses:
- Smaller Build: Weighs significantly less and lacks the same body armor.
- Less Combat Experience: Bulls rarely engage in deadly fights outside of farming or sports.
- Vulnerability: Less protection against a rhino’s high-impact attacks.
Find More – Bull Battle comparisons
Find More – Rhino Battle comparisons
✅ References for Bull vs Rhino Fight
- International Rhino Foundation – Rhino Facts
https://rhinos.org/species/ - National Geographic – Rhinoceros
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/rhinoceros - IUCN Red List – Rhinoceros Species
https://www.iucnredlist.org - University of Missouri Extension – Bull Management
https://extension.missouri.edu/publications/g2017 - The Cattle Site – Bull Characteristics
https://www.thecattlesite.com
Hope you enjoyed the Bull vs Rhino Fight! Let me know, What should be the Next Comparison. Leave a comment!





1 Comment