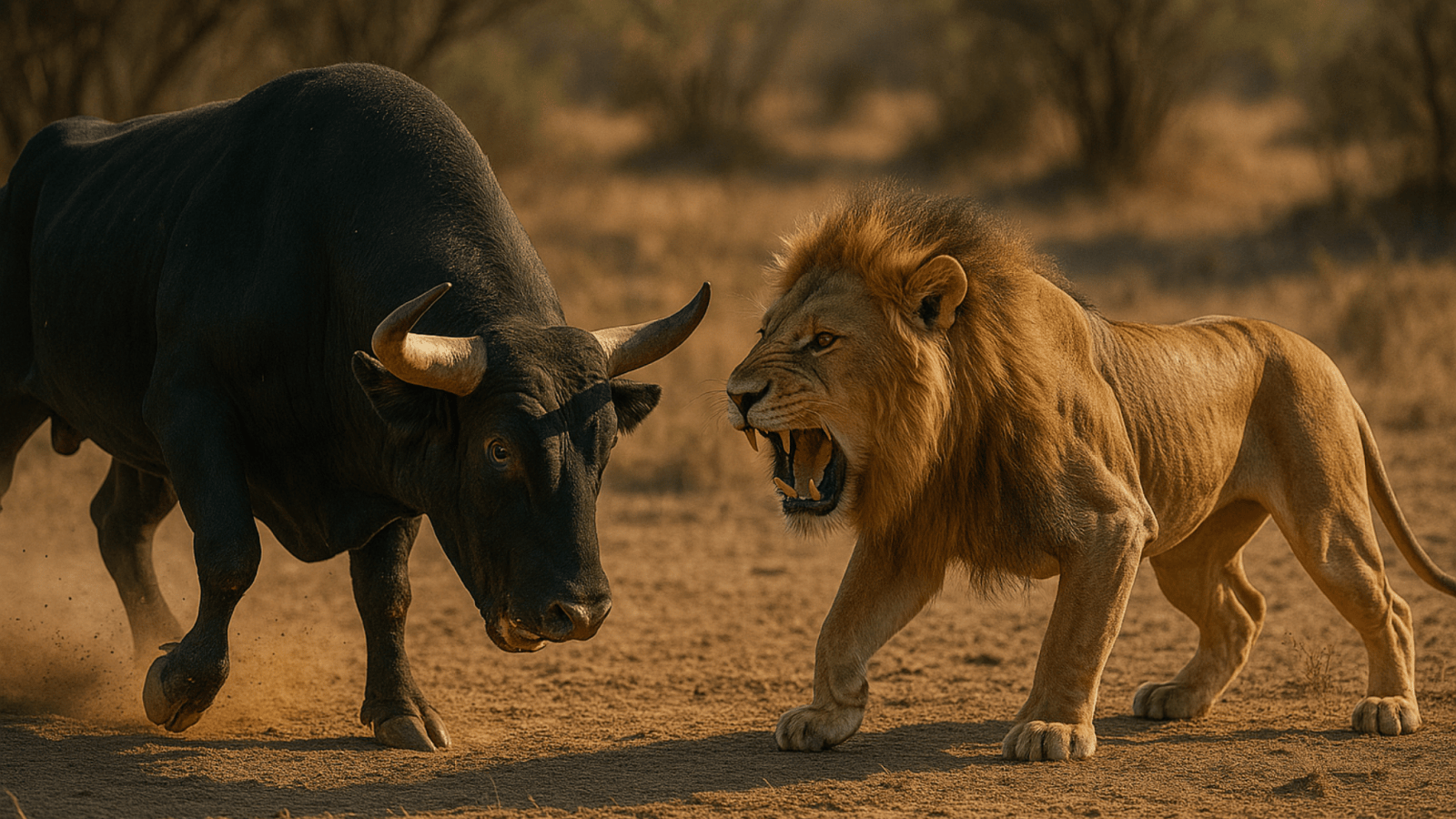
What if heavy Bull vs Lion Who Wins? We all know that in the food chain lion dominates. On the other hand there is a herbivore who can challenge lions. That heavy opponent We bought today is bull. Bull got the raw aggression, and raw strength.
Lion is an apex predator calling the king of the animal kingdom. While lions are expert hunters for bringing down large prey with precision, bulls are massive, muscular animals with deadly horns and an unstoppable charge.
Here lion represents with predatory instinct; the other, sheer brute force. just imagine these two titans were to meet in battle, who would win? In this dramatic comparison of Bull vs Lion who wins, we dive into their physical attributes, combat skills, natural instincts and more to find out the final winner scientifically as well as in a physical fight.
1. Body Specifications
| Subtopic | Bull (Bos taurus) | Lion (Panthera leo) | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Height | 1.5–1.8 m at shoulder | 1.2 m at shoulder | Bull |
| Average Length | 2.4–3.5 m | 2.5–3.3 m (excluding tail) | Draw |
| Weight | 700–1,200 kg (bull breeds) | 150–225 kg (male lion) | Bull |
| Body Structure | Stocky, barrel-chested, muscular | Lean, muscular, agile | Draw |
| Bone Density | Very high (dense limb bones) | Lighter bones for speed | Bull |
| Muscle Mass | High, especially in shoulders | High, especially in hind limbs | Bull |
| Horns/Weapons | Horns (up to 80 cm) | Claws & teeth | Draw |
| Skin Thickness | Thick (hide for protection) | Thinner skin, more agile | Bull |
| Neck Strength | Powerful for pushing/fighting | Strong for gripping prey | Bull |
| Endurance | High in short combat bursts | Moderate | Bull |
Category Winner: Bull – heavier and muscular than the lion.
2. Coat and Coloration
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Color | Black, brown, red, white (varied) | Golden tan | Draw |
| Pattern | Usually solid | Plain, with darker manes (males) | Draw |
| Camouflage Use | Minimal; prey species | Excellent in grasslands | Lion |
| Melanin Variation | Present (black bulls) | Present (black-maned lions) | Draw |
| Seasonal Shedding | Yes | Yes | Draw |
| Hair Texture | Coarse hide fur | Fine fur with thick mane (males) | Lion |
| Mane Function | None | Protection during fights | Lion |
| Thickness | Thick in some breeds | Moderate | Bull |
| Thermoregulation | Strong via hide and body mass | Strong via panting | Draw |
| Grooming Habits | Licks and brushes | Licks and social grooming | Lion |
Category Winner: Lion – Suited for the protection and enhance fighting skills with camouflage.
3. Habitat and Range – Bull vs Lion Who Wins
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic Range | Worldwide (domesticated) | Africa & small parts of India | Bull |
| Habitat Type | Farms, grasslands | Savannas, scrublands, grasslands | Lion |
| Environmental Tolerance | Cold & warm climates | Prefers warmer climates | Bull |
| Natural Distribution | Artificial introduction by humans | Natural predator | Lion |
| Adaptability | Extremely adaptable | Moderately adaptable | Bull |
| Urban Proximity | Often near humans | Rarely | Bull |
| Altitude Range | Sea level to 4,000+ m | Up to ~2,000 m | Bull |
| Territory Range | Confined unless free-roaming | 20–400 km² | Lion |
| Migration Tendency | None | May move with prey | Lion |
| Domestication Status | Fully domesticated | Wild | Lion |
Category Winner: Draw – Each excels in its respective environment.
4. Diet and Hunting
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diet Type | Herbivore | Carnivore | Lion |
| Typical Food | Grass, grains | Zebras, wildebeest, buffalo | Lion |
| Hunting Behavior | None (grazes) | Group coordination by lionesses | Lion |
| Kill Strategy | N/A | Suffocation bite to neck or muzzle | Lion |
| Caloric Intake | ~30,000–40,000 kJ/day | ~15,000–20,000 kJ/day | Bull |
| Hunting Success Rate | N/A | ~30% (lionesses) | Lion |
| Prey Weight Range | N/A | Up to 1,000 kg | Lion |
| Offensive Strategy | Charges if threatened | Ambush and wrestle prey | Lion |
| Aggression During Feeding | Competitive over food | Highly aggressive around kills | Lion |
| Food Storage | None | Rare, eats on site | Lion |
Category Winner: Lion – Master predator with killing skills and strategy.
5. Strength and Bite Force
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bite Force (PSI) | Not applicable | 650 PSI | Lion |
| Horn Strength | Massive force during goring | N/A | Bull |
| Headbutting Force | Over 1,000 kg of force | N/A | Bull |
| Claw Strength | None | Razor-sharp claws with puncture ability | Lion |
| Neck Muscle Strength | Massive, used to push and ram | Strong, used for choking prey | Bull |
| Jaw Muscle Strength | Weak (grazing) | Extremely strong | Lion |
| Lift/Push Capacity | Can push several hundred kg | Can drag ~2x body weight | Bull |
| Strike Force | High-impact forward momentum | Agile strike using claws and jaw | Bull |
| Grappling Ability | Poor | High (uses limbs and teeth in tandem) | Lion |
| Overall Damage Potential | Blunt force trauma | Puncture and bleed-based attacks | Draw |
Category Winner: Draw – Lion has precision killing tools, but bull has brute force.
6. Speed and Agility – Bull vs Lion Who Wins
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Speed | 40–50 km/h | Up to 80 km/h | Lion |
| Acceleration | Moderate | Very fast burst acceleration | Lion |
| Turning Agility | Poor | High agility for cornering | Lion |
| Vertical Leap | ~1 m | Up to 3.5 m | Lion |
| Maneuverability | Limited | Excellent for a predator | Lion |
| Reaction Time | Moderate | Fast reflexes | Lion |
| Ground Grip | Hooves – stable on flat terrain | Padded paws – adaptable on various terrain | Lion |
| Terrain Adaptability | Best on flat, dry land | Excels in tall grass, rocky, or uneven areas | Lion |
| Sprint Duration | Short burst (few seconds) | 100 m sprint range | Lion |
| Combat Mobility | Limited to forward rush or turn | Highly dynamic in fight | Lion |
Category Winner: Lion – Superior in all mobility-related metrics.
7. Senses – Bull vs Lion Who Wins
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision Acuity | Decent, but color-blind | Excellent night vision | Lion |
| Hearing Range | Good (~20 Hz to 35 kHz) | Very sharp (~20 Hz to 60 kHz) | Lion |
| Smell Sensitivity | Strong olfactory abilities | Very acute sense of smell | Draw |
| Night Vision | Poor | 6x better than humans | Lion |
| Field of View | ~330° (wide, panoramic) | ~180° (binocular) | Bull |
| Sound Localization | Moderate | Excellent directional hearing | Lion |
| Communication Calls | Low-frequency grunts or bellows | Roars, growls, moans heard up to 8 km | Lion |
| Vibration Detection | Average – limited to ground impact | Highly sensitive paw pads | Lion |
| Threat Awareness | Reactive | Proactive and predictive | Lion |
| Sensory Coordination | Limited coordination | Sharp coordination of vision + hearing | Lion |
Category Winner: Lion – Powerful in sensory awareness and combat-useful senses.
8. Reproduction and Lifespan
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestation Period | ~283 days | ~110 days | Lion |
| Litter Size | Typically 1 calf | 2–4 cubs | Lion |
| Sexual Maturity | 12–15 months | 2–3 years | Bull |
| Breeding Frequency | Controlled breeding in captivity | Every 2 years or more | Bull |
| Offspring Survival | Very high in farms | Low (~50% cub mortality) | Bull |
| Lifespan (Wild) | 15–20 years | 10–14 years | Bull |
| Lifespan (Captivity) | Up to 25 years | Up to 20 years | Bull |
| Parental Care | Provided by humans | Female lions only | Bull |
| Mating System | Polygynous | Polygynous | Draw |
| Reproductive Control | Fully managed (domesticated) | Natural selection | Bull |
Category Winner: Bull – Domestication ensures higher survival and longevity.
9. Social Behavior
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Structure | Solitary or herd (human-managed) | Prides (6–30 individuals) | Lion |
| Male-Male Interaction | Competitive (dominance fights) | Highly competitive for control of pride | Draw |
| Cooperation | Rare (no teamwork) | Coordinated hunting and defense | Lion |
| Territory Defense | Fights over territory or mates | Patrol and defend territories | Lion |
| Communication Type | Grunts, body posture | Vocalizations, scent marking, visual cues | Lion |
| Parental Role | None (in males) | Females raise cubs cooperatively | Lion |
| Aggression Display | Charging, headbutts | Roars, posturing, fights | Lion |
| Social Intelligence | Moderate | High (knows hierarchy and role) | Lion |
| Conflict Resolution | Fight or flee | Dominance battles, rarely fatal | Lion |
| Grooming & Bonding | Minimal (licking or scratching posts) | Frequent social grooming | Lion |
Category Winner: Lion – Rich social behavior with teamwork and communication.
10. Conservation Status – Bull vs Lion Who Wins
| Subtopic | Bull | Lion | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Status | Domesticated – Not evaluated | Vulnerable | Bull |
| Global Population | Over 1.5 billion | ~20,000–25,000 (wild) | Bull |
| Population Trend | Stable/increasing | Decreasing | Bull |
| Major Threats | None (human-managed) | Habitat loss, poaching | Bull |
| Protection Laws | Not needed | CITES Appendix II, National laws | Lion |
| Breeding Programs | Agricultural breeding | Captive breeding in conservation parks | Draw |
| Human Conflict | Minimal (except bulls escaping) | High (cattle raids, retaliation killings) | Bull |
| Conservation Priority | Low | High | Lion |
| Captive Management | Extensive | Limited, requires wild gene diversity | Bull |
| Risk of Extinction | None | Moderate without intervention | Bull |
Category Winner: Bull – Fully secure under domestication, no conservation risks.
Face-to-Face Fight: Bull vs Lion Who Wins?
In a face to face battle between a bull and a lion, the outcome depends on scenarios:
- In an open, fair 1-on-1 fight, the bull’s massive size, strong horns, and goring ability give it the edge. A charging bull can impale or trample even a full-grown male lion.
- However, lions are not foolish they rarely engage full-grown bulls alone. Lions typically target sick, young, or isolated bovines, and they rely on ambush rather than brute strength.
- The lion could win if it catches the bull by surprise, going for the throat or spine. But the bull’s thick neck and skin make that difficult, especially in frontal encounters.
- In most face-to-face scenarios, the lion risks serious injury, which it cannot afford in the wild.
Final Verdict: Bull Wins
Why the Bull Wins:
- Greater Size and Strength: Up to 1,200 kg vs 190 kg.
- Devastating Horn Attacks: Can fatally gore even predators.
- Durability: Built for physical punishment.
- Not Prey Behavior: Bulls will fight rather than flee.
Why the Lion Loses:
- Too Small for Direct Attack
- Not Built for Long Fights
- Ambush Predator – Not ideal in frontal combat
- High Risk of Injury
Interesting Facts – Bull vs Lion Who Wins
Bull
-
Bulls are much heavier and more muscular than cows, often weighing between 1,500 and 2,200 pounds.
-
They have thick necks, large heads, and strong, bony ridges above their eyes for protection.
-
Bulls grow thick, short horns that are used for fighting and defense.
-
Their bodies are built for power, with strong legs and a hump on their shoulders.
-
Bulls use their horns and strength to fight for dominance in the herd.
-
They can be very aggressive, especially when threatened or challenged.
-
Bulls communicate with body language and posturing.
-
The hair on their neck and head is often curlier and acts as extra protection.
-
Bulls have excellent endurance and can sustain physical exertion for a long time.
-
They are herbivores, eating mostly grass and plants.
Lions
-
Lions are the only big cats that live in groups, called prides, which can have up to 15 members.
-
Male lions have a thick mane around their neck, making them look bigger and protecting them during fights.
-
Adult male lions weigh between 330 and 550 pounds, while females are slightly smaller.
-
Lions are apex predators with powerful jaws, sharp claws, and strong muscles.
-
They hunt mainly at night and rely on teamwork to catch large prey.
-
A lion’s roar can be heard up to 8 kilometers away.
-
Lions have excellent night vision and a strong sense of hearing.
-
They can run up to 50 miles per hour in short bursts.
-
Lions sleep up to 20 hours a day to save energy.
-
They are known as the “king of the jungle” but actually live mostly in grasslands and savannas.
Conclusion – Bull vs Lion Who Wins
So, in the fierce showdown of bull vs lion who wins, the bull comes out on top in a fair, one-on-one duel. The lion is undoubtedly a skilled hunter, but the bull’s sheer size, defensive capabilities, and horn power make it an incredibly difficult opponent to bring down.
Final Score: Bull – 6 | Lion – 3 | Draw – 1
In nature, this is why lions hunt in groups and rarely take on healthy bulls alone.
References
- IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
- BBC Earth – “Big Cats: Lions vs Buffalo”
- Journal of Animal Science – Muscle and bone mass in bulls
- National Geographic – Lion hunting behaviors
- Animal Diversity Web – Panthera leo and Bos taurus profiles
Read More – Sloth Bear vs Lion – Brutal Scientific Winner?





Leave a Reply